They are mostly focusing on hi-tech industries now. The government since then has always been a champion of economic and social restructuring.
Malaysias economic growth in comparative perspective from 1960-90 is set out in Table 4.

. As of 2018 Malaysia has posted a GDP per capita of RM44679. For the sake of economy of Malaysia government is undertaking long term economic plans to upgrade the manufacturing sector to a whole new level. The Transition to Modern Economic Growth.
The impact of the pandemic pushed the economy into negative territory recording a 56 contraction in 2020. Primary production remains important. This growth of Malaysian economy continued to grow at a rate of 6 from 2011 to 2015.
Malaysias economy has been transformed since 1970 from one based primarily on the export of raw materials rubber and tin to one that is among the strongest most diversified and fastest-growing in Southeast Asia. The period 18701920 saw massive growth in Malayas trade initially propelled by the export of tin and later by rubber and was facilitated with the opening of the Suez Canal in 1870 which greatly reduced shipping times between Europe and Asia. The NDP was formerly known as the New Economic Policy.
This raises the risk of stagflation with potentially harmful. An Economic History of Malaysia circa 18001990. As per the International Monetary Fund IMF the Malaysian economy is set to recover further from the Covid-19 downturn and projected a GDP growth of about 575 in 2022.
The 2018 labour productivity of Malaysia was measured at 55360 per worker and is significantly higher than in neighbouring Thailand 30840 Indonesia 23890 The Philippines 19630 and Vietnam. The country is a major producer of rubber and palm oil exports considerable quantities of petroleum and natural gas and is. Malaysia has a long vision of future for their economic strategy.
The real total GDP gross domestic product in Malaysia is expected to grow by 758 by 2025. An Economic History of Malaysia c1800-1990. Malaysia Economic Growth.
From year 1957 where Malaysia had announced independence till the year 1970 Malaysia was an agriculture oriented country which produces tin rubber oil and gas and palm oil. Overview Of The Economy Of Malaysia. Malaysia Q4 GDP Growth Beats Estimates.
GDP per capita is now higher than in a number of OECD economies while poverty and income inequality have declined considerably. Malaysia has sustained over four decades of rapid inclusive growth reducing its dependence on agriculture and commodity exports to become a more diversified modern and open economy. The country recorded a GDP growth rate of 50 in 2015.
It introduced the New Development Policy NDP in a bid to balance wealth redistribution and economic growth. This page provides - Malaysia GDP Growth Rate -. Malaysia gdp growth rate for 2020 was -559 a 989 decline from 2019.
Malaysia is the 4th largest economy of South East Asia and has continued to perform strongly in recent years due to a strong global demand for. 51 rows It is calculated without making deductions for depreciation of fabricated assets or for depletion and degradation of natural resources. The subject of economic growth.
Malaysia had a GDP by PPP of 8156 billion and a nominal GDP of 2962 billion in 2015. In fact Malaysian economic-history writing has a long tradition of association with public issues for most of the works have originated with their authors interests in contemporary economic problems treated historically and often in the context of regional or international trade with the objective. For 2022 the central bank maintained its GDP outlook at 53-63 with inflation projected to average between 22 and 32.
As a source of gold tin and exotics such as birds feathers edible birds nests aromatic woods tree resins etc. The Gross Domestic Product GDP in Malaysia expanded 390 percent in the first quarter of 2022 over the previous quarter. Absolute poverty dropped to 15 percent in 1990 and has been.
In 2015 Malaysias PPP GDP per capita was estimated at 2630020 while the nominal GDP per capita stood at 9776206. Malaysias economy grew by 36 yoy in Q4 of 2021 rebounding sharply from a 45 contraction in Q3 and above market consensus of a 33 gain. That said potential Covid-19 flare-ups and the prospect of general elections in 2022 cloud the.
GDP is projected to expand at a swifter pace in 2022 bolstered by a new phase of the pandemic management strategy. This sector had dedicated 60 of Gross Domestic Products GDP between these years. Economic Overview For the latest updates on the key economic responses from governments to address the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic please consult the IMFs policy tracking platform Policy Responses to COVID-19.
During the 1970s Malaysias economy is primarily focused on exporting tin and rubber. The benefits of economic growth after Independence was shared more equally as real GDP growth in the post-Independence period led to rapid advances in the average standard of living and to reductions in absolute poverty. Compounding the damage from the COVID-19 pandemic the Russian invasion of Ukraine has magnified the slowdown in the global economy which is entering what could become a protracted period of feeble growth and elevated inflation according to the World Banks latest Global Economic Prospects report.
In 2021 GDP growth rebounded to 31. The history of the Malaysian economy can explain through the structural change process. This growth rate is twice the 6 rate of average annual growth of GDP in the 1960s and one and a half times the high 75 per annum GDP growth in the 1970s Chee 1982a.
At the same time education is instrumental in generating economic growth by boosting productivity and enabling populations to contribute more effectively. The average annual growth rate in this sector of 12 has been consistently higher than that of any other sector in the economy during the last two decades. The GNI gross national income in Malaysia is forecast.
Malaysia gdp growth rate for 2019 was 430 a. Moreover recovering activity among key trading partners and higher commodity prices should sustain exports. 51 rows Malaysia economic growth for 2020 was 33666B a 768 decline from 2019.
The Transition to Modern Economic Growth Posted Sun 2001-07-08 2000 by backend. The economy of Malaysia is the third largest in Southeast Asia in terms of GDP per Capita and the 34th largest in the world according to the International Monetary Fund. Although the economic growth rates of modern Malaysia h ave not been equal to the East Asian NICs South Korea Taiwan and Hong Kong Malaysian econom ic growth perked along at five to seven percent per year from.
GDP Growth Rate in Malaysia averaged 115 percent from 2000 until 2022 reaching an all time high of 1730 percent in the third quarter of 2020 and a record low of -1610 percent in the second quarter of 2020. Malaysia has a long history of internationally valued exports being known from the early centuries AD. Knowledge of Malaysias economic history is essential for understanding the countrys present day social demographic and economic achievements and challenges.

2022 53 Uncertainties In Malaysia S Economic Recovery By Cassey Lee Iseas Yusof Ishak Institute

Asean Economies Poised For Robust Recovery With 6 Real Gdp Growth In 2021 Says Globaldata Globaldata

Malaysia S Economic Growth And Transition To High Income An Application Of The World Bank Long Term Growth Model

2022 53 Uncertainties In Malaysia S Economic Recovery By Cassey Lee Iseas Yusof Ishak Institute
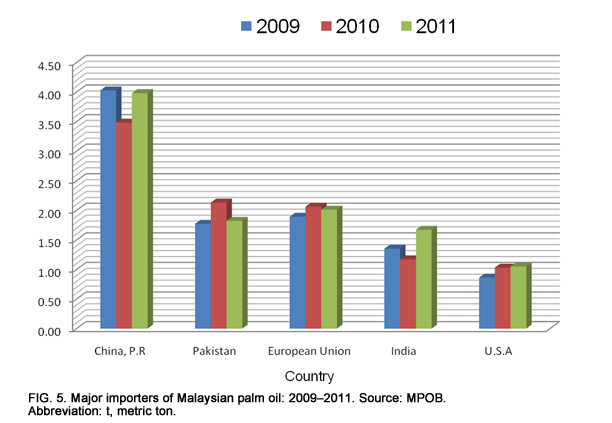
Malaysia Economic Transformation Advances Oil Palm Industry

Malaysia Gross Domestic Product Gdp Growth Rate 2027 Statista
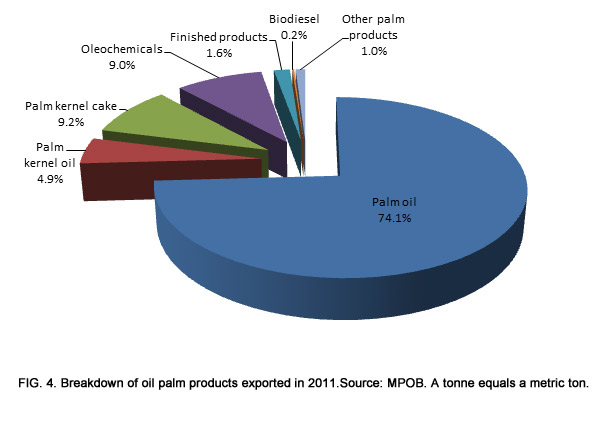
Malaysia Economic Transformation Advances Oil Palm Industry

Divergent Recoveries In Asia History Is Not Destiny Imf Blog

Malaysia Inflation Rate 2010 2024 Statista

2022 53 Uncertainties In Malaysia S Economic Recovery By Cassey Lee Iseas Yusof Ishak Institute
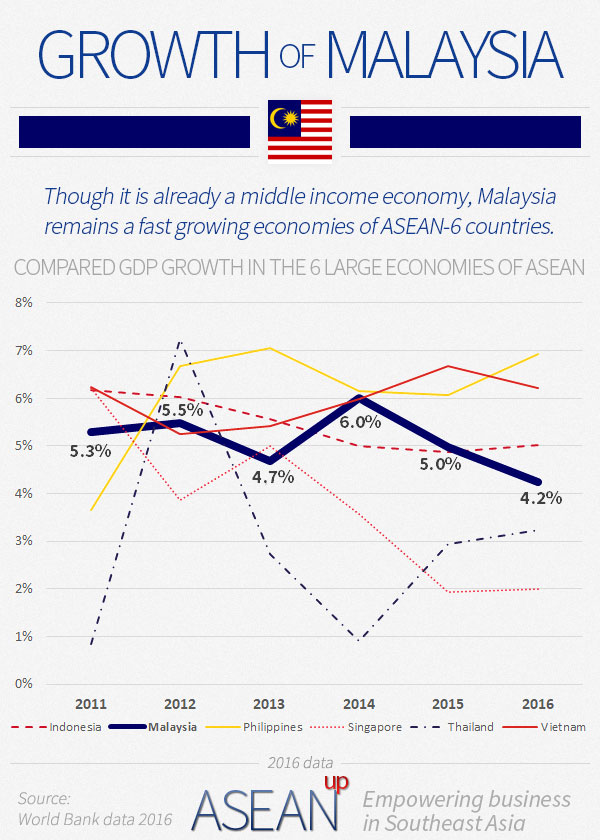
Overview Of Business In Malaysia Asean Up
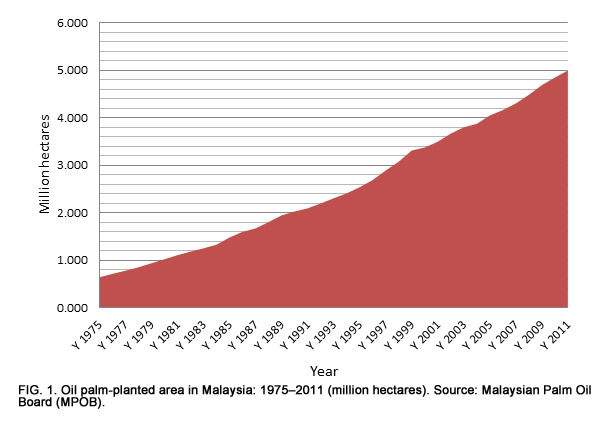
Malaysia Economic Transformation Advances Oil Palm Industry

Malaysian Ringgit Exchange Rate Usd To Myr News Forecasts

Malaysia To Achieve High Income Status Between 2024 And 2028 But Needs To Improve The Quality Inclusiveness And Sustainability Of Economic Growth To Remain Competitive
Malaysia S New Economic Model Making Choices Dq En

Malaysia Resources And Power Britannica

Malaysia S Economic Growth And Transition To High Income An Application Of The World Bank Long Term Growth Model

Malaysia Inflation Rate 2010 2024 Statista

Asean Economies Poised For Robust Recovery With 6 Real Gdp Growth In 2021 Says Globaldata Globaldata
